6 most frequently asked questions about electric vehicle batteries
What's inside an electric car battery, how long it takes to charge, how quickly it loses capacity, how much it costs, how to replace it, and what to do with the old one. We answer the most frequently asked questions of electric car owners and anyone planning to join an EV club. Some general information What is an electric car battery? An electric car battery is a large battery compartment with dimensions of approximately 200x150x15 cm and a weight of [...]
Content:
What's inside an electric car battery, how long it takes to charge, how quickly it loses capacity, how much it costs, how to replace it, and what to do with the old one. We answer the most frequently asked questions of electric car owners and anyone planning to join the EV club.
Some general information
What it is
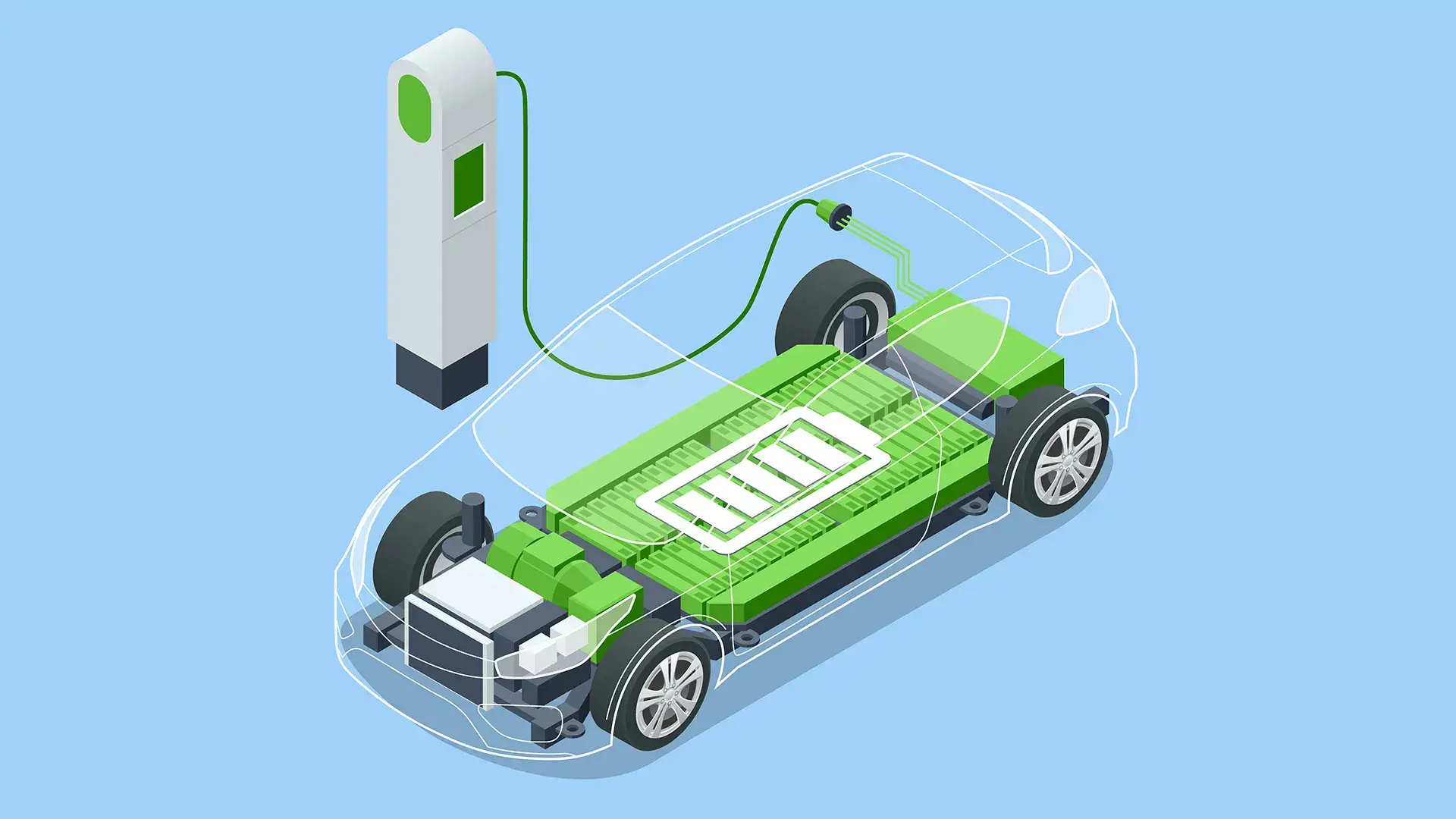
The battery of an electric vehicle is a large battery compartment with dimensions of approximately 200x150x15 cm and a weight of approximately 540 kg. It is located in the bottom of the car and is attached to the body with brackets. If you cut it open, you will see a number of blocks, each of which consists of several thousand compact lithium-ion cells. In Tesla, these cells are similar to ordinary finger batteries, in Nissan Leaf or Chevrolet Bolt they have a pack shape, and in Audi they are prismatic. Such a battery generates as much energy as more than 1,500 laptop batteries. To control the temperature of the battery during operation, it is equipped with a cooling system.
Types
There are different types of batteries: lithium-ion, aluminium-ion, lithium-sulphur, lithium-iron phosphate, and metal-air. Most often, electric vehicles use lithium-ion batteries. They have a high energy density, high power, low self-discharge, no memory effect, and a fairly long service life (8-10 years). However, they are expensive, can overheat and explode.
Despite the high cost of lithium-ion batteries and their questionable safety, almost nothing can compete with them in terms of power and the number of charge-discharge cycles. Developers are constantly searching for the optimal formula for battery production: safe, with low production costs, long service life, easy disposal, fast charging time and maximum efficiency (with a specific energy of 400 Wh/kg or more).
Who produces
Batteries for electric vehicles are produced in Asia: China, South Korea, and Japan. These companies are BYD, Panasonic, LG Chem, Samsung SDI, Farais, AESC Automotive Energy Supply Corp. The leader among all manufacturers is the Chinese company CATL, thanks to active government subsidies. Panasonic produces batteries for Tesla cars, while BYD fills electric buses with batteries. Many manufacturers locate production facilities in Europe and America.
Outlook.
The most promising are graphene-based batteries. It is used to improve battery properties, for example, by adding it to electrodes and increasing their conductivity. Such batteries are much lighter than lithium-ion batteries and do not explode. The specific capacity is 5 times higher than that of a lithium-ion battery (1000 Wh vs. 200 Wh per 1 kg of weight). Tesla Model S with a graphene battery can travel 1,013 km on a single charge instead of 334 km, and can be charged in less than 10 minutes.
For all their excellent characteristics, graphene batteries and other modern developments (e.g, batteries based on materials derived from seawater), should have filled the market long ago. However, manufacturers continue to improve lithium-ion batteries created in the 70s, and investors are reluctant to invest in the development of new technologies. After all, this requires millions of dollars, which will not pay off for the reasons that new batteries will be tested for years, then they will go through a long period of adaptation in the market and very slowly increase the interest of the buyer. We can only hope that graphene will be able to change this situation for the better, as a huge amount of capital has already been invested in the development of batteries based on it.
In the meantime, graphene batteries remain a project of the future, so let's find out what a typical lithium-ion battery looks like using a home assembly as an example. Craftsmen from the Ukrainian YouTube channel KREOSAN assemble lithium-ion batteries for welding machines, electric bicycles, etc. The same principle is used in electric vehicles, but the assembly is not handicraft, but industrial.
How soon will I need to replace the battery of my electric vehicle?
The average service life of electric vehicle batteries is 5-8 years (if charged every day). This does not mean that after these years, the battery will lose 100% of capacity and will need to be replaced. In fact, it will retain about 70% and can continue to be used further, but you will have to accept the fact that the driving distance per charge will decrease. For example, after 5 years of operation, the Nissan Leaf can travel 100-130 km on a single charge from the declared 160 km. Keep in mind that not only time, but also operating mode with the number of charge-discharge, heating and overheating cycles, the presence of cooling or its absence (like the Nissan Leaf), depending on the design features of the car.
The rate of capacity decline also depends on the specific model of electric vehicle. Observing the behaviour of the Tesla Model S and Nissan Leaf batteries shows that the capacity is actively decreasing over 5 years of operation: the first 1-2 years, the range decreases by 5-10%, and over the next 3 years - by another 20-30%. After that, the process stops and becomes stable: the decrease is only 0.5% annually.
If you use fast charging technology too often (more often than 4-5 times a week), the battery degrades 1.5-2 times faster, so it is better to charge it fully in a parking lot or at night, not while driving. It is worth using the same principle as when charging gadgets: keep the charge in the range of 20-80%, avoiding complete discharge. The worst thing you can do is regularly discharge the battery to 0% and then leave it in this state for a long time. Otherwise, it will lose its buffer stock and quickly deteriorate.
To extend the battery life, make sure that it does not overheat (a comfortable temperature is 21°C). Do not leave the electric vehicle in the open sun and look for shade for it.
Is it possible to repair or replace the battery of an electric vehicle?
It is possible and necessary if the battery has lost most of its capacity. But it's not as easy as replacing a smartphone or laptop battery, for example. You can't just take it out and replace it with a new one:
It is necessary to make sure that the connectors and fasteners of the new battery are suitable for a specific model of electric vehicle - that is why the battery is selected individually;
After installation, the electronic systems need to be reprogrammed - to "introduce" the battery control unit to the car's on-board computer;
If the battery is damaged (for example, by a protrusion or flood on the road surface), it does not require a complete replacement. Due to the fact that this is not a monolithic structure, but interconnected blocks (their number varies from 16 to 48 pieces), only damaged areas can be replaced, provided that moisture does not get inside the structure, which will destroy the battery.
How much does a new battery for an electric car cost?
Battery prices are getting lower every year. According to Energy Trend's forecasts the cost of the battery in 2020 will be less than $150 /kWh. For comparison, in 2016, the price of lithium-ion batteries was $300-300/kWh, and in 2018 it was already $180-200/kWh. The cost of one kilowatt-hour is planned to be reduced through new packaging designs, changes in supply chains and reduced production costs.
In Ukraine, you can buy a new unit for the Nissan Leaf at a price of about $100 and, accordingly, for $4-5 thousand the whole battery. Tesla is much more expensive and more blocks need to be assembled: 1 block costs $1000, and a whole battery of 16 blocks costs $16000. Owners of electric vehicles save money by buying second-hand units. They are cheaper, but it should be borne in mind that their capacity will be 5-15% less than originally stated.
Where should I take my used battery?
There are no electric vehicle battery recycling plants in Ukraine. At the same time, it is also impossible to simply take the battery to a landfill, as it contains dangerous toxic substances that pose a great threat to the environment. Ukrainian owners of electric vehicles can take advantage of a win-win situation: reuse the battery as a source of stationary energy storage.
For example, if you have solar panels installed on your roof, you can connect used batteries to them, charge them and use them as a backup in the autonomous power supply system of the house. In some countries, this issue has been approached on a large scale: in Japan, such batteries power streetlights, in Paris they support the operation of elevators, and in Amsterdam they illuminate an entire stadium.
In Germany and Finland, there are companies that are engaged in mass and safe battery recycling, but they do not have direct cooperation with Ukraine. Therefore, you cannot just call and hand over your battery. All that remains is to wait until these companies' representative offices or recycling funds appear in Ukraine, and now try to make the most of the batteries for your own needs. In the future, as the number of electric vehicles and batteries for them grows, reuse will become the norm.
The German waste management company Duesenfeld has invented a technology for the safe disposal of used batteries. It differs from other methods in that the battery components are not incinerated but crushed using nitrogen gas, which eliminates all reactions in the battery. After recycling, only ferrous and non-ferrous metals and cathode residues with manganese, cobalt, and nickel remain in the battery. All of this can be reused.
How long does it take to charge the battery?
In Ukraine, there are charging stations in almost all cities. Their capacity is 2-23 kW. There are also fast ones: up to 50 kW, which charge the battery in 30-40 minutes (the charge is enough for 80-100 km of run). Fast stations are suitable for electric vehicles that are adapted to three-phase networks and can receive 22 kW and above. AC charging stations are now actively spreading across Ukraine because they are cheaper than DC fast stations and easier to put into operation.
It is beneficial to charge your car at home from an outlet at night. From 23:00 to 7:00, all consumed electricity is estimated at only 0.5 of the tariff. These 8 hours are enough to charge an electric car from a home outlet (Tesla takes longer to charge: a full charge with a 75 kWh battery and 3 kW charging power takes more than a day).
To charge at home, you need a three-phase socket with a current of 16 A and a power of 11 kW. A typical 220 V outlet has a power rating of no more than 3 kW, which is why charging can take about 33 hours. To charge an electric vehicle from a household outlet, you must install a ground connection and protect the wiring from voltage surges.
Is charging cheaper than filling up with petrol?
The more expensive electricity is, the more expensive it is to charge an electric vehicle. If you charge it from a home outlet, you pay utility tariffs, and if you use a network of charging stations, you pay prices that are individual to each company.
The cost of recharging from the mains charger depends on the power of the station and the charging speed. The approximate price per 1 kW is UAH 5, if charging is fast - UAH 7-9. For example, to charge a Nissan Leaf with a 24 kWh battery for a run of more than 100 km, you can spend about UAH 150, and if you charge it at home at the night rate, you will only spend UAH 15-20. There are free charging stations, but they take longer to charge an electric car and you still have to find them in the city.
For comparison, a conventional car with an internal combustion engine costs about UAH 240-300 per 100 km to charge.
Results.
So far, there are no electric vehicles so old that users can find out exactly how long the battery lasts and when it needs to be replaced. Therefore, for a few years, you don't have to think about recycling the battery and replacing it (in 2020, this will only apply to owners of 2010 Nissan Leaf models). By the time mass battery replacement and recycling is required, more advanced recycling/reuse mechanisms will be available and prices will fall. But even without this, an electric car is becoming more convenient and economical than a car with an internal combustion engine every year.






